你应该使用哪个异步 Apex 框架?这篇博客提供了一个自动为你选择 Batchable 或 Queueable Apex 的解决方案。
Batchable 和 Queueable 是 Salesforce 平台上开发人员可用的两种主要异步框架。在处理记录时,您可能会思考应该使用哪一种。在本文中,我们将介绍一种替代方案,它能自动在 Batchable 和 Queueable 这两种 Apex 框架之间选择最合适的选项——这样您就可以专注于需要实现的逻辑,而不必担心选择哪种异步执行方式最佳。
让我们来探讨一种结合两者优点的方法。Batchable 和 Queueable 经常用于:
- 执行 API 调用 (因为在同步触发器代码或直接在计划作业中不允许进行调用)
- 处理数据 (由于 Salesforce 的限制,在同步调用代码时无法处理这些数据)
话虽如此,这两个框架之间存在一些有趣的区别 (您可能已经熟悉),这些区别在使用时会产生明显的优缺点。
Batchable Apex:
- 启动较慢,在 Batchable 块之间移动较慢
- 在其 start 方法中可以查询多达 5000 万条记录
- 在任何给定时间只能有五个批处理作业同时运行
- 可以在队列中维护批处理作业,以便在五个并发批处理作业繁忙时启动,但灵活队列中最多只能有 100 个批处理作业
Queueable Apex:
- 执行快速,实现简单
- 仍受 Apex 查询行数限制为 50,000 条记录
- 在同步事务中最多可以启动 50 个 queueable apex 作业
- 在异步事务中只能将 1 个 queueable 作业加入队列
这些优缺点为我们提供了一个独特的机会,可以抽象异步进程的定义方式,并创建可重用的内容,无论您需要处理多少记录。
让我们来看一个实现示例,然后详细了解这种抽象是如何工作的。
首先,让我们看一个设计的使用示例
这个例子假设您正在使用一个 B2C(企业对消费者)Salesforce 组织,其中账户名称始终需要与联系人姓名匹配,并且每个账户只能关联一个联系人。请注意,在我们的 ContactAsyncProcessor 示例中,唯一需要存在的逻辑恰恰与这条业务规则相关:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class ContactAsyncProcessor extends AsyncProcessor {
protected override void innerExecute(List records) {
Map<Id, Account> accountsToUpdate = new Map<Id, Account>();
for (Contact con : (List) records) {
accountsToUpdate.put(
con.AccountId,
new Account(
Id = con.AccountId,
Name = con.FirstName + ' ' + con.LastName
)
);
}
update accountsToUpdate.values();
}
}
// and then in usage
new ContactAsnycProcessor()
.get('SELECT AccountId, FirstName, LastName FROM Contact')
.kickoff();
当然,这只是一个非常简单的示例 —— 它没有展示诸如 Contact.AccountId 为空、处理中间名等更复杂的情况。不过,这个例子确实展示了子类化如何帮助简化代码。在这里,你不需要担心示例查询会返回多少结果,也不用考虑是否应该使用 Batchable 或 Queueable 实现 —— 你可以专注于业务规则本身。
那么,AsyncProcessor 父类最终会是什么样子呢?让我们来看看幕后发生了什么。
创建一个共享异步处理器
首先,在尝试整合 Batchable 和 Queueable 接口时,我们需要注意一些有趣的技术限制:
- 批处理类必须是外部类。虽然在语法上可以将内部类声明为 Batchable,但如果尝试通过 Database.executeBatch 执行内部类,将会抛出异常。
- 这种异步异常只会在日志中显示,而不会在同步上下文中直接返回给调用者,这可能会造成误导,因为执行不会像传统异常那样立即停止。
- 队列类可以是内部类,但实现了 Database.Batchable 和 Database.Stateful 的外部类不能同时实现 System.Queueable。
您希望这个框架具有灵活性和可扩展性,无需进行任何修改。它应该能够:
- 获取一个查询或记录列表。
- 评估查询或列表中包含的记录数量。
- 检查是否低于某个阈值 (子类应能修改此阈值) - 如果低于阈值则启动 Queueable,否则启动 Batchable。
下面的图表展示了需要同步执行和异步执行的内容:
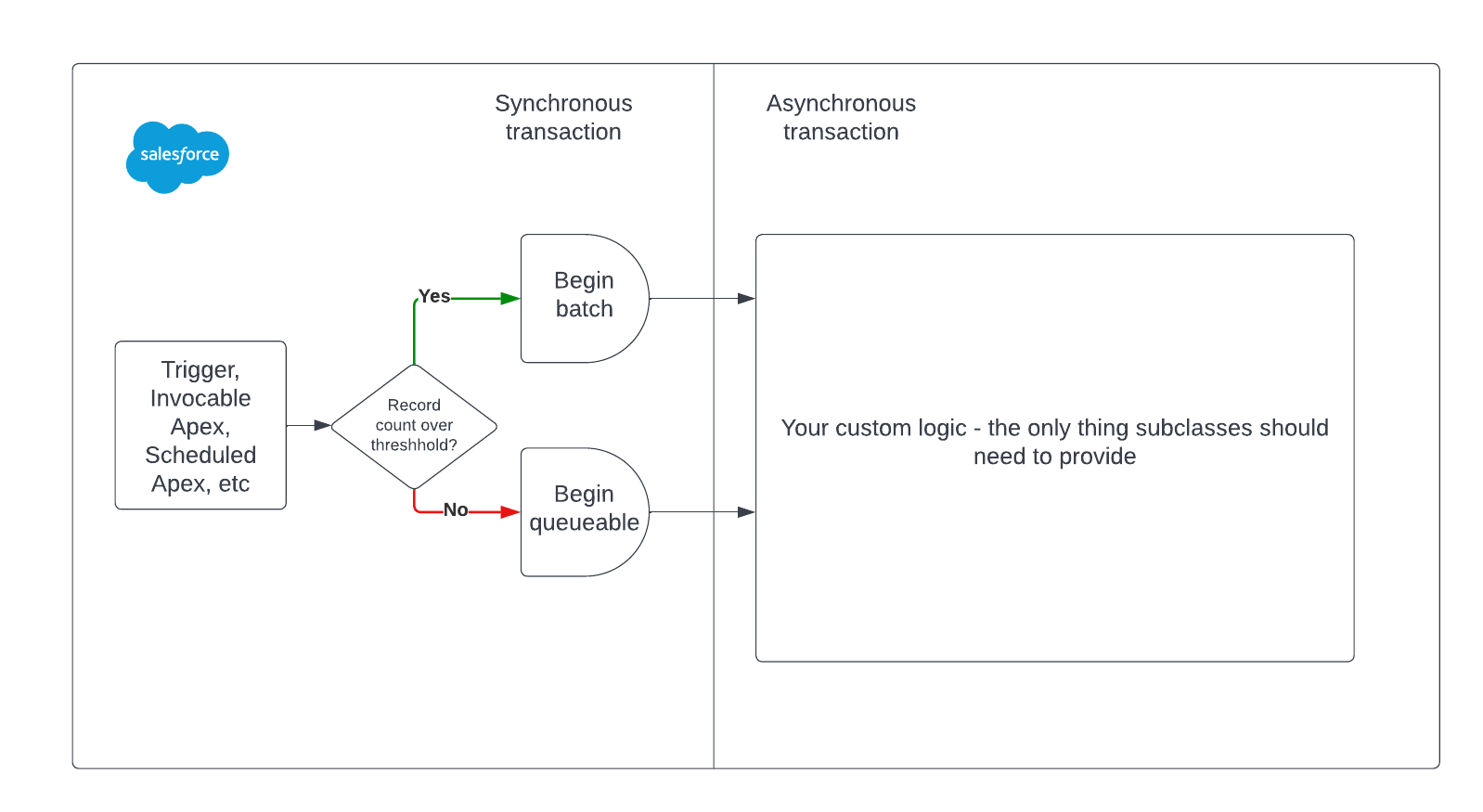
这些限制可以帮助指导共享抽象的整体设计。例如,在异步处理记录之前,你应该有一种方式与这个类进行交互 —— 这正是定义接口的绝佳位置。
1
2
3
public interface Process {
String kickoff();
}
由于 Batchable 类需要是外部类,因此您可以先在那里实现 Process.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
public abstract without sharing class AsyncProcessor implements Database.Batchable, Database.RaisesPlatformEvents, Process {
private static final String FALLBACK_QUERY = 'SELECT Id FROM Organization';
private Boolean hasBeenEnqueuedAsync = false;
private Boolean getWasCalled = false;
private String query;
private List records;
public String kickoff() {
this.validate();
return Database.executeBatch(this);
}
public Database.QueryLocator start(Database.BatchableContext bc) {
return Database.getQueryLocator(
this.query != null ? this.query : FALLBACK_QUERY
);
}
public void execute(
Database.BatchableContext bc,
List localRecords
) {
this.hasBeenEnqueuedAsync = false;
this.innerExecute(this.records != null ? this.records : localRecords);
}
public virtual void finish(Database.BatchableContext bc) {
}
protected abstract void innerExecute(List records);
private void validate() {
if (this.getWasCalled == false) {
throw new AsyncException(
'Please call "get" to retrieve the correct Process instance' +
' before calling kickoff'
);
}
}
}
不要太担心 query 和 records 实例变量,它们很快就会发挥作用。以上代码的关键部分如下:
AsyncProcessor类被标记为抽象类。innerExecute方法也是抽象的Database.Batchable接口所需实现的方法已经被定义了。- 已经定义了
kickoff方法,它满足Process接口
通过初始化一个新的 DataProcessor 的子类,然后调用 get 方法,你会收到 DataProcessor.Process 接口的一个实例。
- 要么提供一个基于字符串的查询
- 或通过提供记录列表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
public abstract without sharing class AsyncProcessor implements Database.Batchable, Database.RaisesPlatformEvents, Processor {
public Process get(String query) {
return this.getProcess(query?.toLowerCase(), null);
}
public Process get(List records) {
return this.getProcess(null, records);
}
protected Process getProcess(String query, List records) {
this.getWasCalled = true;
this.records = records;
this.query = query;
Integer recordCount = query == null
? records.size()
: Database.countQuery(
query.replace(query.substringBeforeLast(' from '), 'select count() ')
);
Boolean shouldBatch = recordCount > this.getLimitToBatch();
Process process = this;
if (shouldBatch == false && this.getCanEnqueue()) {
// AsyncProcessorQueueable will be shown next
process = new AsyncProcessorQueueable(
this
);
}
return process;
}
protected virtual Integer getLimitToBatch() {
return Limits.getLimitQueryRows();
}
private Boolean getCanEnqueue() {
// only one Queueable can be started per async transaction
return this.hasBeenEnqueuedAsync == false ||
(this.isAsync() == false &&
Limits.getQueueableJobs() < Limits.getLimitQueueableJobs());
}
private Boolean isAsync() {
return System.isQueueable() || System.isBatch() || System.isFuture();
}
}
上述代码中最重要的部分是这段:
1
2
3
4
5
6
Integer recordCount = query == null
? records.size()
: Database.countQuery(
query.replace(query.substringBefore(' from '), 'select count() ')
);
Boolean shouldBatch = recordCount > this.getLimitToBatch();
shouldBatch 布尔值可以判断最终启动的是 batch 还是 queueable 进程!
最后是 AsyncProcessorQueueable 的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
// in AsyncProcessor.cls
private class AsyncProcessorQueueable implements System.Queueable, Process {
private final AsyncProcessor processor;
public AsyncProcessorQueueable(AsyncProcessor processor) {
this.processor = processor;
this.processor.hasBeenEnqueuedAsync = true;
}
public String kickoff() {
this.processor.validate();
if (this.processor.getCanEnqueue() == false) {
return this.processor.kickoff();
}
return System.enqueueJob(this);
}
public void execute(System.QueueableContext qc) {
if (this.processor.records == null && this.processor.query != null) {
this.processor.records = Database.query(this.processor.query);
}
this.processor.innerExecute(this.processor.records);
this.processor.finish(new QueueableToBatchableContext(qc));
}
}
private class QueueableToBatchableContext implements Database.BatchableContext {
private final Id jobId;
public QueueableToBatchableContext(System.QueueableContext qc) {
this.jobId = qc.getJobId();
}
public Id getJobId() {
return this.jobId;
}
public Id getChildJobId() {
return null;
}
}
queueable 也可以实现 System.Finalizer 接口,它允许你只使用 BatchApexErrorEvent 的平台事件来处理错误。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
// in AsyncProcessor.cls
@TestVisible
private static BatchApexErrorEvent firedErrorEvent;
private class AsyncProcessorQueueable implements System.Queueable, System.Finalizer, Process {
public void execute(System.QueueableContext qc) {
System.attachFinalizer(this);
// plus the logic shown above
}
public void execute(System.FinalizerContext fc) {
switch on fc?.getResult() {
when UNHANDLED_EXCEPTION {
this.fireBatchApexErrorEvent(fc);
}
}
}
private void fireBatchApexErrorEvent(System.FinalizerContext fc) {
String fullLengthJobScope = String.join(this.getRecordsInScope(), ',');
Integer jobScopeLengthLimit = 40000;
Integer textFieldLengthLimit = 5000;
BatchApexErrorEvent errorEvent = new BatchApexErrorEvent(
AsyncApexJobId = fc.getAsyncApexJobId(),
DoesExceedJobScopeMaxLength = fullLengthJobScope.length() >
jobScopeLengthLimit,
ExceptionType = fc.getException().getTypeName(),
JobScope = this.getSafeSubstring(
fullLengthJobScope,
jobScopeLengthLimit
)
.removeEnd(','),
Message = this.getSafeSubstring(
fc.getException().getMessage(),
textFieldLengthLimit
),
Phase = 'EXECUTE',
StackTrace = this.getSafeSubstring(
fc.getException().getStacktraceString(),
textFieldLengthLimit
)
);
firedErrorEvent = errorEvent;
EventBus.publish(errorEvent);
}
private List getRecordsInScope() {
List scope = new List();
for (
Id recordId : new Map<Id, SObject>(this.processor.records).keySet()
) {
scope.add(recordId);
}
return scope;
}
private String getSafeSubstring(String target, Integer maxLength) {
return target.length() > maxLength
? target.substring(0, maxLength)
: target;
}
}
总的来说,整个思想是子类将扩展外部的 AsyncProcessor 类,这将强制它们定义 innerExecute 抽象方法。
-
他们可以调用
kickoff来启动他们的流程,而不必担心查询限制或底层平台将使用哪个异步框架。- 所有的平台限制,如:每个异步事务只能启动一个队列,都会自动为你处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
private Boolean getHasAlreadyEnqueued() { return this.isAlreadyAsync || (System.isQueueable() == false && System.isBatch() == false && System.isFuture() == false && Limits.getQueueableJobs() < Limits.getLimitQueueableJobs()); }
- 你不必再担心任何给定的查询会检索到多少条记录; 如果你有超过每个查询行数限制的危险,该过程将自动为你分批进行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
protected Process getProcess(String query, List records) { // .... Boolean shouldBatch = recordCount > this.getLimitToBatch(); Process process = this; if (shouldBatch == false && this.getHasAlreadyEnqueued() == false) { process = new AsyncProcessorQueueable( this ); } return process; }
-
子类可以在必要时选择实现 Database.Stateful 和 Database.AllowsCallouts 之类的接口来扩展自己的实现。由于这些是标记接口,不需要子类来实现额外的方法,因此最好是只让绝对需要此功能的子类选择该功能 (而不是总是让它们在
AsyncProcessor本身实现).1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
public class HttpProcessor extends AsyncProcessor implements Database.AllowsCallouts { protected override void innerExecute(List records) { HttpRequest req = new HttpRequest(); req.setMethod('POST'); req.setEndpoint('callout:Named_Cred_Name'); req.setBody(JSON.serialize(records)); new Http().send(req); } }
- 所有的平台限制,如:每个异步事务只能启动一个队列,都会自动为你处理。
因为,默认情况下,子类只需要定义他们自己的 innerExecute 实现,所以您可以从创建独立的 Batchable 和 Queueable 类时通常附带的所有其他仪式中解放出来。具体到你的实现的逻辑 (例如:如果您正在为每条记录执行一个 callout, 并跟踪执行了多少 callout), 仍然需要被测试。
这里有一个更复杂的例子,显示了如果你超过 callout 限制,如何递归地重新启动进程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class BulkSafeHttpProcessor extends AsyncProcessor implements Database.AllowsCallouts {
protected override void innerExecute(List records) {
while (records.isEmpty() == false && Limits.getCallouts() < Limits.getLimitCallouts()) {
HttpRequest req = new HttpRequest();
req.setMethod('POST');
req.setEndpoint('callout:Named_Cred_Name');
req.setBody(JSON.serialize(records.remove(0));
new Http().send(req);
}
// recursively restart until there's no more records
// to process
if (records.isEmpty() == false) {
this.kickoff();
}
}
}
作为另一个标记接口示例,下面是使用 Database.Stateful 的样子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class CounterProcessor extends AsyncProcessor implements Database.Stateful {
private Integer counter = 0;
public override void finish(Database.BatchableContext bc) {
System.debug(this.counter);
}
protected override void innerExecute(List records) {
this.counter += records.size();
}
}
一旦掌握了 AsyncProcessor 中的所有复杂部分,你就可以纯粹地专注于逻辑。这确实有助于保持你的类小而有条理。
对异步处理器进行单元测试
在这里,我们将只展示一个测试,证明 AsyncProcessor 的子类在超过配置的排队限制时会自动批处理。您也能够通过访问该项目存储库来访问所有测试类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
@IsTest
private class AsyncProcessorTests extends AsyncProcessor {
private static Integer batchLimit = Limits.getLimitQueryRows();
private static Boolean executeWasFired = false;
private static Boolean finishWasFired = false;
public override void finish(Database.BatchableContext bc) {
finishWasFired = true;
}
protected override void innerExecute(List records) {
executeCallCounter++;
executeWasFired = true;
}
protected override Integer getLimitToBatch() {
return batchLimit;
}
@IsTest
static void allowsBatchLimitToBeAdjusted() {
batchLimit = 0;
// here we have to actually do DML so that the batch start method
// successfully passes data to the batch execute method
insert new Account(Name = AsyncProcessorTests.class.getName());
Test.startTest();
new AsyncProcessorTests().get('SELECT Id FROM Account').kickoff();
Test.stopTest();
Assert.areEqual(
1,
[
SELECT COUNT()
FROM AsyncApexJob
WHERE
Status = 'Completed'
AND JobType = 'BatchApexWorker'
AND ApexClass.Name = :AsyncProcessorTests.class.getName()
]
);
Assert.isTrue(executeWasFired);
Assert.isTrue(finishWasFired);
}
}
总结
AsyncProcessor 模式让我们专注于实现我们的异步逻辑,而不必直接指定确切的工作执行方式。此模式的更高级用户可能更喜欢覆盖批处理大小等信息,或者允许使用/不使用共享查询上下文之类的信息。虽然可以考虑许多额外的细微差别,但此模式是一个很好的方法,也可以在您需要使用异步 Apex 时按原样使用。查看完整的源代码以了解更多信息。